 West
Nile Virus West
Nile Virus
Introduction:
West Nile (WN) virus has emerged in recent years in temperate regions of
Europe and North America, presenting a threat to public, equine, and
animal health. The most serious manifestation of WN virus infection is
fatal encephalitis (inflammation of the brain) in humans and horses, as
well as mortality in certain domestic and wild birds.
History: West
Nile virus was first isolated from a febrile adult woman in the West
Nile District of Uganda in 1937. The ecology was characterized in Egypt
in the 1950s. The virus became recognized as a cause of severe human
meningoencephalitis (inflammation of the spinal cord and brain) in
elderly patients during an outbreak in Israel in 1957. Equine disease
was first noted in Egypt and France in the early 1960s. The appearance
of WN virus in North America in 1999, with encephalitis reported in
humans and horses, may be an important milestone in the evolving history
of this virus.
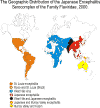 Geographic
Distribution: West Nile virus has been described in Africa, Europe,
the Middle East, west and central Asia, Oceania (subtype Kunjin), and
most recently, North America. Recent outbreaks of WN virus encephalitis
in humans have occurred in Algeria in 1994, Romania in 1996-1997, the
Czech Republic in 1997, the Democratic Republic of the Congo in 1998,
Russia in 1999, the United States in 1999-2000, and Israel in 2000.
Epizootics of disease in horses occurred in Morocco in 1996, Italy in
1998, the United States in 1999-2000, and France in 2000. In the U.S.
through September 2000, WN virus has been documented in Connecticut,
Maryland, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York,
Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, and the District of Columbia. In 2001, WN
had been documented in North Florida with confirmed human cases. Geographic
Distribution: West Nile virus has been described in Africa, Europe,
the Middle East, west and central Asia, Oceania (subtype Kunjin), and
most recently, North America. Recent outbreaks of WN virus encephalitis
in humans have occurred in Algeria in 1994, Romania in 1996-1997, the
Czech Republic in 1997, the Democratic Republic of the Congo in 1998,
Russia in 1999, the United States in 1999-2000, and Israel in 2000.
Epizootics of disease in horses occurred in Morocco in 1996, Italy in
1998, the United States in 1999-2000, and France in 2000. In the U.S.
through September 2000, WN virus has been documented in Connecticut,
Maryland, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York,
Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, and the District of Columbia. In 2001, WN
had been documented in North Florida with confirmed human cases.
Classification:
- Family: Flaviviridae
- Genus: Flavivirus
Japanese Encephalitis Antigenic Complex
- Complex
includes: Alfuy, Cacipacore, Japanese encephalitis, Koutango,
Kunjin, Murray Valley encephalitis, St. Louis encephalitis, Rocio,
Stratford, Usutu, West Nile, and Yaounde viruses.
- Flaviviruses:
share a common size (40-60nm), symmetry (enveloped, icosahedral
nucleocapsid), nucleic acid (positive-sense, single stranded RNA
approximately 10,000-11,000 bases), and appearance in the electron
microscope.
Useful
Links - Florida West Nile Virus and EEE (Eastern Equine Encephalitis)
|